Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is a chronic degenerative-dystrophic process that damages the disc and vertebral body of the thoracic spine. It is less common than osteonecrosis of the cervical or cervical spine. However, this doesn't mean it doesn't cause trouble for the person. The thoracic spine tumors manifest mainly with back and chest pain, but can also cause pain in the heart and abdomen, similar to angina or liver cramps. In rare cases, bone necrosis of the thoracic spine causes the development of muscles in the lower extremities, a decrease in their sensitivity, disorders of the pelvic organs. Treatment includes the use of drugs and non-medicinal methods, sometimes even surgery. From this article, you will learn about symptoms of thoracic spondylolisthesis and disease treatment methods.
Chest spine
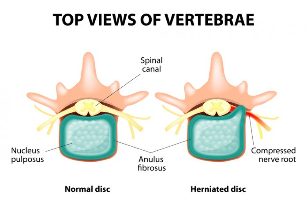
The thoracic spine is represented by 12 vertebrae, between vertebrae there are discs. The disc consists of a pulp nucleus and a ring-shaped fibroid. Pathological changes in these discs, as well as in the lateral joints, proliferation of bone spines along the edges of the vertebral body, dystrophy in the ligaments of the spine, andImmediate cause of back pain.
It should be understood that osteonecrosis, which is a disease, rarely affects only part of the spine. Usually this process is diffuse, more or less pronounced in different parts of the spine.
Several structural features of the thoracic spine make it less affected by bone destruction compared to other spinal regions. Please list the following features:
- poor mobility of the thoracic spine;
- presence of vertebral junctions with ribs (combined with sternum creates a firm, less traumatic thoracic frame);
- small thickness of the disc;
- physiological kyphosis (bends in the anterior and posterior direction with protruding protrusions towards the back) of the thoracic spine, and therefore the maximum axial load falls on the anterior part, not the posterior part of the disc.
Another feature is not the structure, but the development of osteonecrosis of the thoracic spine, which also determines the frequency of less pain in the thoracic spine, which is the existing morphological basis of necrosisbone necrosis in this part may remain clinically "dumbfounded" for a long time. That is, there are changes, but they do not disturb the patient.
And yet, when there are provoking factors, such as sedentary lifestyles (including years of working at desks or driving cars), injuries, poor posture, back musclessagging, strenuous physical labor in forced postures, thoracic spine degeneration shows his true face.
Symptoms of necrosis of the thoracic spine

The main clinical symptom of necrosis of the thoracic spine as well as other organs is pain. Back pain, chest pain, even pain in internal organs. In medicine, one often distinguishes some pain syndromes (and not just pain) of osteonecrosis disease of the thoracic spine. In total, they are divided into two groups:
Reflection- ; Compress
- .
The reflex syndrome is a clinical manifestation of spinal receptor stimulation. These are the receptors for the ligaments, the synapses, the disc, and receive pathological impulses during the degeneration of the bone. In addition to pain, reflex syndrome can be accompanied by muscle tension, vegetative disorders of soft tissue and internal organs. Such changes are based on the following fact: stimulation of the receptors leads to the propagation of stimuli to the neighboring structures of the spinal cord (more precisely to the segments of the spinal cord). And these can be nerve cells responsible for sweating of a certain area of skin, regulating the temperature of that region, participating in ensuring the functioning of internal organs (heart, liver, intestines, etc. ). etc. ), maintains the muscles and blood vessels that supply all of these structures. And when stimulation is transmitted to these nerve cells, corresponding symptoms of disruption of activity of certain formations arise. Therefore, such a situation is entirely possible when the pain in the abdomen or in the heart area is caused by bone necrosis of the thoracic spine.
Compression syndrome occurs when a nerve root becomes compressed (less often stretched) as it leaves the disc, tissue of the spinal cord or the vessels that feed it. Compression syndrome is almost always caused by an existing herniated disc. The most common is the herniation of the subnoracic segments. Depending on the direction and location of the hernia, a person experiences certain symptoms. This can be presented as follows:
- Median (middle) hernia accompanied by development of symmetrical muscle weakness in both legs, loss of sensitivity in them. At the same time, there is no typical pain syndrome for compression of the nerve roots;
- lateral (lateral) hernia manifested exclusively by pain associated with compression of the nerve root; The
- lateral intermediate herniation combines the clinical symptoms of the two previous groups, with only muscle weakness and dominant sensory disturbances in the bulging disc.
What types of syndromes are considered syndrome of necrosis of the thoracic spine? Let's talk in more detail about the types of reflex and compression syndrome of this degree.
The reflex syndrome
Dorsago- sudden pain in the thoracic spine. It has a sharp nature, often described by the patient as a dagger strike. Basically, it is felt between the scapula, it can be delivered to the heart, the sternum. The patient is afraid of moving and even breathing deeply, because the pain is more intense (as if it shot back) from this. Usually, these symptoms occur after a long time in a fixed uncomfortable position, while performing monotonous work. A sudden movement then causes low back pain in people with necrosis of the thoracic spine. When palpating the thoracic spine reveals the tension of the vertebral muscles in the form of rollers and their soreness.
Sometimes such pain can be considered a heart attack, the patient seems severe and sudden. However, the scanned ECG was not abnormal, and sublingual administration of nitroglycerin did not eliminate the pain.
Back painis a type of thoracic acute reflex syndrome. It is a pain syndrome that occurs gradually. The pain can be localized on any part of the back or chest. Soreness, dullness, sometimes slight burning (related to stimulation of vegetative structures). This condition is exacerbated when movements of the spine, bend, rotate around its axis, cough or sneeze, drive on uneven roads.
Pain may be felt along the intercostal region on one or both sides. This feature is due to nerve conduction (intercostal nerves and vessels located in the intercostal space). In this case, the pain is called intercostal pain, similar to the pain caused by shingles.
If the pain is localized in the anterior chest wall, it is also known as stomach pain. However, it can only be felt in some places with the back intact. For example, in the area of the xiphoid process or at the binding site of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Usually, due to the aching and dull nature of pain, it is difficult to pinpoint the exact location of the pain: something inside the chest, or in the superficial soft tissue area.
Back pain may be accompanied by a spinal strain reflex, which is more pronounced on the side of the pain. In this case, of course, the muscle tension is not as pronounced as in a similar situation in the lumbar spine. However, when you are touched, muscles feel squeezed and the touch itself is uncomfortable or painful. It is also painful to feel palpitations and vertebrae in the area affected by bone necrosis.
The reflex syndrome in thoracic spondylosis is much more common than the squeezing syndrome.
Compression syndrome
Squeezing of the nerve rootsis primarily accompanied by pain syndrome. The pain is happening in nature. The direction of pain spread corresponds to the path of the nerve fibers. In the case of thoracic necrosis, these are intercostal spaces. Since certain nerve fibers form tangles that are involved in covering the internal organs, you may experience pain inside your chest or abdomen. Pain increases with movement, leaning, coughing, sneezing, laughing (because the tension of the root increases). In the area where the roots are internally compressed, sensitive disorders: tingling, numbness, tingling sensation can be observed. Touching this area may not be possible. In the case of a pinched nerve for a long time, movement disturbances may occur, i. e. the muscles within it are weakened. The muscles gradually shrink. However, movement disorders are rare, as they are the most recent symptom of the onset of all symptoms. Usually, a person seeks medical help in stages of pain and sensory disturbances.
Spinal cord compressionpresents with bipedal weakness with simultaneous increase in muscle tone (if the spinal cord is pinched in the lower thoracic spine, then muscle tone decreases). Possible foot pathological symptoms (Babinsky et al. ). Lower extremities lose sensitivity, the sensation of touching hot and cold is no different, just touch and sting. In the case of severe compression of the spinal cord, urination disorders may occur.
Compression of blood vessels,supplying to the spinal cord, leads to the development of myeloid ischemia, that is, malnutrition of spinal tissues. This, as well as compression of the spinal cord, is accompanied by the development of muscle weakness (the patient says "leg has failed"), loss of sensation and pelvic disturbances.
It is fair to say that the compression of the spinal cord and its vessels during bone destruction of the thoracic spine is very, very rare.
The vegetative components of bone resorption of the thoracic spine

Since nerve fibers coming from the thoracic spine contain autonomous leads, irritation or invasion of these fibers can be associated with autonomic symptoms. This could be:
- dry and flaky skin at separate nerve attachment regions;
- local violation of sweating and conditioning (also according to the inner region);
- chills of lower extremities, brittle toenails;
- pain that simulates diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (eg, gastritis, peptic ulcer, cholecystitis, etc. );
- pain in the kidney, practically unrelated to kidney disease (no change in urine and ultrasound);
- pain in the heart area, very similar to angina and even myocardial infarction.
The peculiarity of such pain may be that a person may not feel pain in the back. This initially confuses both the patient and the medical staff when seeking medical help. However, carrying out some additional research methods can rule out the pathology of internal organs, and then bone necrosis of the thoracic spine is considered the cause of that pain.
Treatment of necrosis of the thoracic spine
All treatments for thoracic spondylosis are divided into medicinal and non-medicinal. In most cases, only a combination of the two groups works and the disease goes into remission. Although you need to understand that it is simply not possible to completely eliminate necrosis of the thoracic spine. Degenerative process can be suspended, slowed down but it does not have the opposite development.
Medicines
The main directions of drug exposure to osteonecrosis of the thoracic spine are pain elimination, removal of muscle tension, improvement of tissue microcirculation and nutrition.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used successfully to eliminate pain syndrome. Drugs of this group have the ability to reduce inflammatory processes, eliminate pain and prevent platelet aggregation. Drugs are prescribed, on average, for 7-14 days. This is usually enough to eliminate the pain. Many of them are available in different forms (tablets, capsules, solution for injection, rectal suppositories), which ensure ease of use. The first days of treatment, the drug is used in the form of an injection, after which they are transferred to the form of tablets or suppositories. Similar drugs can be used topically at the same time: on the thoracic spine area. Furthermore, for this purpose, there are also several forms of release: creams, ointments, gels, patches.
Sometimes nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs aren't enough for pain relief. In such cases, use a pain relief mixture. The mixtures are injected into a vein in salt water or glucose.
Live closing has a pretty good and fast analgesic effect. This is a type of medical manipulation, when a drug is injected near the spine in the internal organs, under the skin, into the thickness of the muscle tissue, the perineal layer (directly near the nerve or root). The procedure requires a certain skill and experience from the doctor.
In addition, local irritating and distracting ointments can be used to relieve pain in osteoporosis of the thoracic spine. These are ointments that contain snake venom, bee venom and pepper extracts.
Relieves muscle tension with non-medicinal methods.
Diuretic, hormonal, Escina Lysinat is used to reduce nerve root edema.
To normalize blood circulation, improve tissue nutrition and restore nutrition, Pentoxifylline, Dipyridamole, Complamin, Nicotinic acid are used.
During the osteoporosis of the thoracic spine, B vitamins are shown, which have analgesic and nourishing effects.
When the exacerbation of thoracic spondylolisthesis is captured, you can use drugs that improve the metabolism of the disc and joints. These are the so-called chondroprotectors. These drugs work to stimulate regeneration of cartilage and joints, suspend degenerative processes in the intervertebral discs. They are prescribed for a long time (3-6 months).
Non-medicinal method
These include:
- massage (classical, point, reflex-segment);
- physical therapy exercises;
- stretches spasmodic muscles (there are special techniques, stretching is not done according to the "optional" principle);
- acupuncture; Swimming
- (very helpful for all patients with any bone necrosis localization);
- physiotherapy (ultrasound, electrophoresis, amplipulse, diadynamic currents, sludge therapy, etc. ).
If a herniated mass is formed due to spinal degeneration of the thoracic spinal cord compressing the spinal cord, blood vessels or nerve roots, and causing muscle weakness, dysfunction of the pelvic organs, pronounced pain syndrome(drug resistance), then question is considered regarding surgical treatment performance.
U of the thoracic spine is not a fatal disease, but it does cause a lot of harm to the patient. It limits his life, hinders his work and rest well. The main symptom of necrosis of the thoracic spine is pain. It is not possible to completely get rid of the disease, but it is possible to suspend the degenerative process and minimize its manifestations.







































